LAVIS (Learning and Visual Systems)
Finished Projects
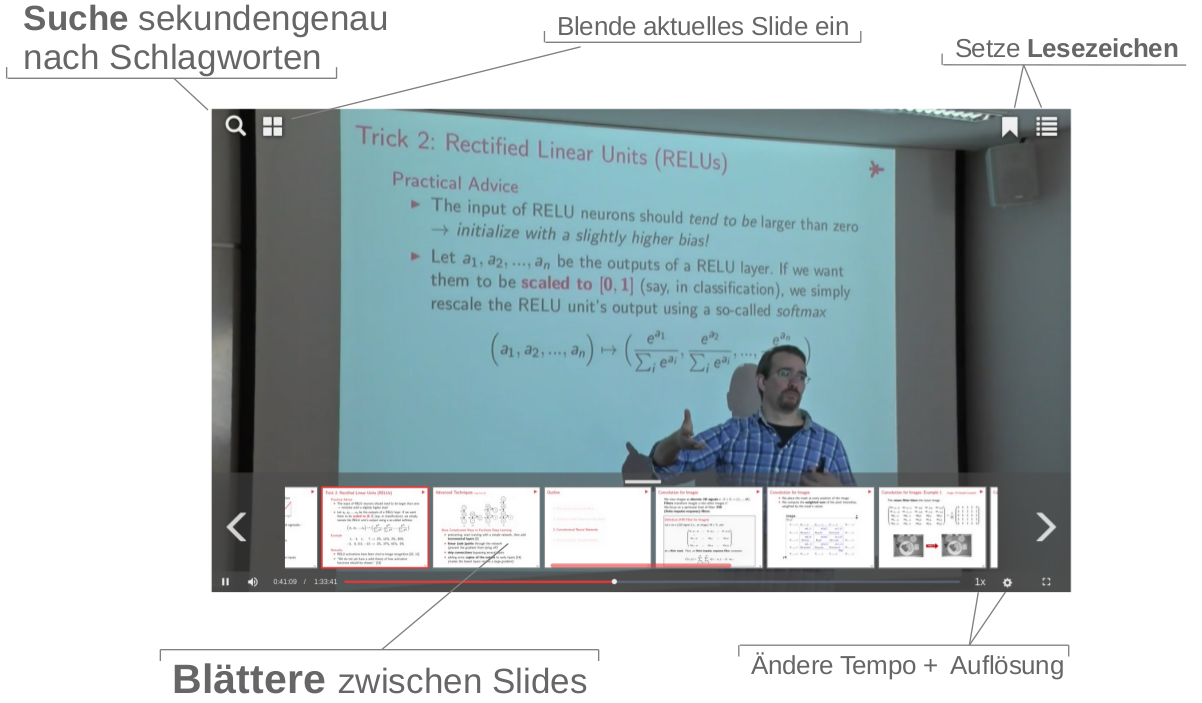
AMIGO
Educational video is the key driver to e-learning, as it offers rich context, flexibility, and personalized learning speed. Interaction possibilities, however, are often limited to a sequential viewing. To overcome this limitation, AMIGO's goal is an interaction with videos just like with PDFs: You can search for text in e-lectures, copy text from them, navigate between pages/slides, get links to interesting stuff, etc. Key to that is an automatic indexer for e-lectures that - given a video and presentation slides - automatically localizes each slide in the video, estimating a pixel- and frame-accurate position of each text box.AMIGO live system (access restricted) | AMIGO paper

AI-Mod
Ziel von AI-Mod ist der Einsatz lernender Verfahren für eine smarte Modellierung von Wertströmen: Mit einer innovativen KI-basierten Lösung sollen Unternehmen Wertströme künftig einfacher simulieren und damit besser gestalten können als heute. Bislang wird allenfalls ein statisches Bild von Wertströmen mit Hilfe von Wertstromdesign und -analyse erhoben, welches eher selten durch eine tiefgreifende Wertstromsimulation ergänzt wird. Das liegt daran, dass die Erstellung eines Wertstrom-Simulationsmodells bislang ein umfassendes Verständnis von Simulationstechnologie erfordert und damit überwiegend Spezialisten vorbehalten ist. In AI-Mod sollen Suchverfahren entwickelt werden, die automatisch statisch modellierte Wertstrom-Graphen interpretieren und im Falle von Modellierungsfehlern in simulationsfähige (d. h. von einer Simulationssoftware fehlerfrei interpretierbare) Wertströme überführen. Um der kombinatorischen Explosion des Lösungsraums zu begegnen, soll die Wertstromkorrektur wie ein Spiel betrachtet werden kann: das Lernverfahren schlägt Züge (= Veränderungen am statisch modellierten Wertstrom) vor. Wenn so ein Wertstrom entsteht, der besser von der Simulationssoftware interpretiert werden kann, gibt es eine positive Rückmeldung, ansonsten eine negative. So lernt der Algorithmus, welche Änderungen an Wertströmen erforderlich sind, um Simulationsfähigkeit zu erreichen. AI-Mod verbindet die Expertise der praxisorientierten Wertstrom-Modellierung der Simplan AG mit den Forschungsarbeiten zu maschinellem Lernen an der Hochschule RheinMain. Als assoziierter Anwendungspartner begleiten die Mercedes-Benz AG und die Siemens Industry Software GmbH das Vorhaben.

Dieses Projekt wird durch das Programm DISTR@L des Landes Hessen gefördert.
Projekt-Website @ lidia-hessen

APOLLON
Virtual reality applications often requires to bake complex light situations for specific objects in a virtual scene into textures, so called lightmaps. These lightmaps can be used in any 3D realtime applications like games or visualization apps. With precalculated lightmaps it is possible to improve the performance and the visual quality in realtime applications. In this project we develop a software tool that supports at least baking of Global Illumination, Ambient Occlusion and Direct Lighting / Shadow Baking. Dieses Projekt (HA-Projekt-Nr. 229/10-05) wurde im Rahmen von
Hessen ModellProjekte aus Mitteln der LOEWE – Landes-Offensive
zur Entwicklung Wissenschaftlich-ökonomischer Exzellenz,
Förderlinie 3: KMU-Verbundprojektvorhaben gefördert.
Dieses Projekt (HA-Projekt-Nr. 229/10-05) wurde im Rahmen von
Hessen ModellProjekte aus Mitteln der LOEWE – Landes-Offensive
zur Entwicklung Wissenschaftlich-ökonomischer Exzellenz,
Förderlinie 3: KMU-Verbundprojektvorhaben gefördert.

ATRIUM
In this R&D project, a new framework will be developed with which the simulation and visualization of various bulk materials can be carried out in real time. In contrast to current simulation methods, a new data-based approach will be used, where the behaviour of the bulk material is predicted with the help of AI instead of being calculated on the basis of physically motivated equations. Using the results from classical calculations, training data is generated and a suitable regression model is developed to train a convolutional neural network to predict the simulation results. This promises a considerable acceleration of the simulation calculation. The saved computing power is then used to achieve a more detailed and realistic visualization or to enable certain simulations even on less powerful devices.
ATRIUM wird durch das Zentrale Innovationsprogramm Mittelstand (ZIM) des Bundesministeriums für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) gefördert.
AUTOMEX
Many simulations like crash-tests, pedestrian vehicle interactions, vibration or noise analysis depend on simplified finite element models, which have to be generated from existing 3D-CAD models. The AUTOMEX project develops automated methods to compute medial axis representations for arbitrarily complex thin-walled components such as synthetic materials and cast metal parts. For further information please visit our project website.
Dieses Projekt (HA-Projekt-Nr. 300/11-45) wurde im Rahmen von Hessen ModellProjekte aus Mitteln der LOEWE – Landes-Offensive zur Entwicklung Wissenschaftlich-ökonomischer Exzellenz, Förderlinie 3: KMU-Verbundprojektvorhaben gefördert.

Code Buddy
Mit Code Buddy soll ein neuartiges KI-System entstehen, welches für Softwareentwickler die Rolle eines Progammier-Partners einnimmt: Code Buddy empfiehlt automatisch vorhandene Lösungen aus der Software-Community – sei es von Kollegen, aus Frage-Antwort-Foren, oder aus Open-Source-Projekten – und adaptiert diese falls geeignet direkt. Um dies zu realisieren, besteht der Forschungsbeitrag in einem neuartigen KI-Ansatz, dessen Training auf großen Datenmengen von Open-Source Code erfolgt. Da keine Daten vorliegen, welche Code-Stellen füreinander relevant sind, wird ein spezieller unüberwachter Ansatz entwickelt, in dem ein neuronales Netz – bestehend aus einer Suchkomponente und einer Generatorkomponente – autonom lernt, zum Füllen von Lücken hilfreiche Code-Passagen zu finden. Wissenschaftliches Kernergebnis ist die Exploration dieses – für die Softwareentwicklung neuartigen – Ansatzes, sowie seine Erprobung in Kooperation mit einem mittelständischen Software-Unternehmen.
Code Buddy wird in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Firmenpartner AOE GmbH durchgeführt. Das Projekt wird durch das Hessische Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Kunst (HMWK) gefördert.
Camera-based Document Capture
Compared to scanners, digital cameras offer a cheap, quick, or even ubiquitious alternative for capturing documents. However, information extraction from the resulting images is hampered by low resolution, noise, and distorsion. These challenges can be tackled by dewarping document images prior to analysis, or by robustifying optical character recognition (OCR) to take low resolution into account.demo | sample paper (dewarping)

DeepCA
Content Analytics is targeted at extracting knowledge from heterogenous data sources, mainly natural language text. Here, recent models based on neural networks (deep learning) open up possibilities for improving search, tagging, categorization, and exploration. DeepCA's mission is to interlink neural models with conventional semantic knowledge modelling using ontologies. A cognitive service for text and knowledge graph analysis will be developed that can easily adapted for the exploration of new domains and leads to innovative solutions for semantic text annotation and search in heterogenous case bases. Through this, DeepCA will form the basis for an end-user centric, efficient knowledge engineering.
DeepCA is conducted in collaboration with the company partners Empolis and SER, and with the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI) and the University of Trier as academic partners. The project is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research.
DeepCA Website
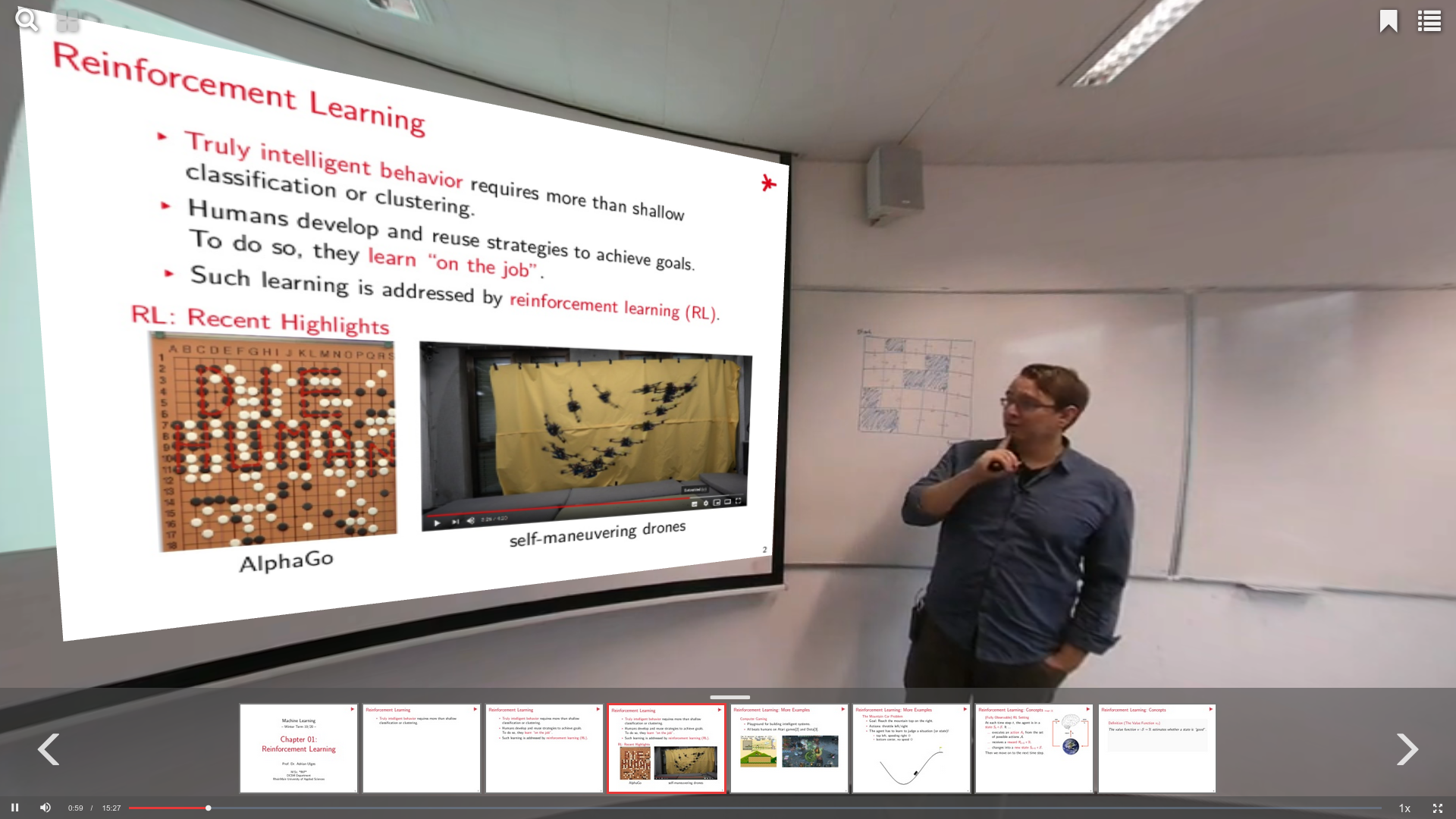
digLL-Innovationsforum VR/AR
Digitale Medien sind ein Fundament der digital gestützten Lehre. Während Bilder, interaktive Fragen oder Videos bereits weit verbreitet sind, besitzen Virtuelle Realität (VR) und Augmentierte Realität (AR) noch neue Potenziale für die Hochschullehre: VR beispielsweise kann Studierenden eine neue Qualität an Erfahrbarkeit und Interaktion ermöglichen, AR kann die Realität nahtlos um zusätzliche Inhalte erweitern. Im Rahmen des beantragten Innovationsforums sollen neue Formen des digital gestützten Lernen und Lehrens mit VR und AR im Kontext der besonderen Anforderungen von Hochschulen konzipiert, untersucht und bewertet werden. Dabei liegt ein besonderes Augenmerk auf die Machbarkeit sowie Übertragbarkeit der gefunden Lösungen über die Grenzen von Hochschulen und Disziplinen hinweg. Im Rahmen von digLL entsteht deshalb unter anderem ein Katalog mit Hochschul-Anwendungen von VR/AR. An der Hochschule RheinMain erweitern wir außerdem unsere Video-Lernplattform AMIGO um die Möglichkeit, Lehrvideos mit dynamischen 3D-Objekten anzureichern.
 Das Innovationsforum VR/AR wird in Kooperation mit der Goethe-Universität Frankfurt und der Hochschule Fulda im Rahmen des Projekts "Digital gestütztes Lernen und Lehren in Hessen" (digLL) durchgeführt.
Das Innovationsforum VR/AR wird in Kooperation mit der Goethe-Universität Frankfurt und der Hochschule Fulda im Rahmen des Projekts "Digital gestütztes Lernen und Lehren in Hessen" (digLL) durchgeführt.

EMIL
Im Rahmen des Forschungsprojekts EMIL wurde eine innovative Möglichkeit geschaffen, Multitouch- und Tangible-User-Interfaces zu erstellen. EMIL kann in der betrieblichen Praxis von Unternehmen genutzt werden, um u.a. Neukunden zu akquirieren und um den Erstellungsprozess solcher Benutzerschnittstellen zu verbessern. Firmen, die mit EMIL erstellte Anwendungen einsetzten, besitzen mit diesen neuartigen Benutzerschnittstellen einen Innovationsvorsprung vor Wettbewerbern. Im Projekt wurde die EMIL-Umgebung erstellt. Diese Umgebung formt einen nutzer-zentrierten Design-Prozess zur Erstellung von Software für interaktive Oberflächen, in dessen Rahmen mit Hilfe der von EMIL bereitgestellten Bibliotheken und Tools interaktive Prototypen erstellt werden. Mit Hilfe dieser Prototypen können Ersteller solcher Software
potenziell neue Aufträge akquirieren, Software näher am Kunden
entwickeln und zur Qualitätssicherung der Usability frühzeitig
mit dem Entnutzer testen. Die EMIL-Umgebung umfasst unter
anderem ein Basis-Framework, ein Autoren-Werkzeug, zwei
Applikations-Frameworks und ein System zur Bereitstellung und
Sammlung von Design-Wissen.
Mit Hilfe dieser Prototypen können Ersteller solcher Software
potenziell neue Aufträge akquirieren, Software näher am Kunden
entwickeln und zur Qualitätssicherung der Usability frühzeitig
mit dem Entnutzer testen. Die EMIL-Umgebung umfasst unter
anderem ein Basis-Framework, ein Autoren-Werkzeug, zwei
Applikations-Frameworks und ein System zur Bereitstellung und
Sammlung von Design-Wissen.

FIBEVID
Key to preserving (often endangered) fish species is a cheap, non-invasive sampling strategy to tackle issues such as population estimation and species association tracking. Current manual sampling methods are expensive, of limited coverage, and come with fish injury and mortality. Therefore, the goal of FIBEVID is to employ underwater computer vision technology for an automated surveying of fish. This includes the construction and deployment of suitable underwater camera rigs, as well as the development of semi-automatic localization, tracking, measuring and classification software for underwater species. FIBEVID is conducted in cooperation with
the National
University of Sciences and Technology (NUST) in Islamabad /
Pakistan. The project is sponsored by the German Academic
Exchange Service (DAAD).
FIBEVID is conducted in cooperation with
the National
University of Sciences and Technology (NUST) in Islamabad /
Pakistan. The project is sponsored by the German Academic
Exchange Service (DAAD).
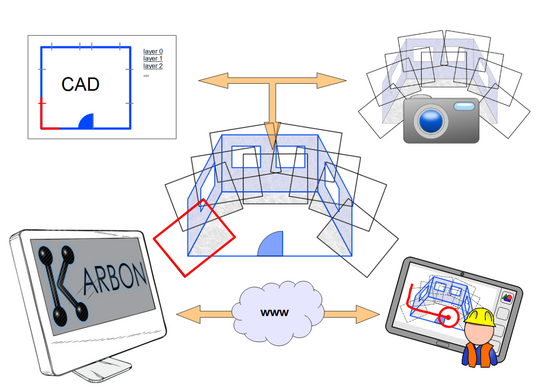
KARBON
Für die Unterstützung von Planungsvorgängen bei der Bauorganisation setzt kARbon Post-WIMP Technologien ein, um Werkzeuge anzubieten, mit denen planende und ausführende Kräfte kollaborativ zusammenarbeiten. Endgeräte wie Tablets bieten dabei eine Plattform für intuitive, leichtgängige Interaktion auf Basis Deiktischer Gesten (Zeigegesten). Ziel von kARbon ist es, eine verteilte Mehrbenutzerkonferenz zu ermöglichen, bei denen sich am Bau beteiligte Personen wie Architekt und Bauleiter über verschiedene Endgeräte von verschiedenen Orten aus virtuell treffen und gemeinsam Arbeitsschritte planen. Durch solche Rücksprachen als erweiterte Form einer Telefonkonferenz wird die Notwendigkeit von realen Treffen reduziert, was besonders bei Projekten mit weit entfernten Partnern von Vorteil ist. Dies verringert zum einen den Kostenaufwand derartiger Treffen,
zum anderen können die Situation vor Ort und die
durchzuführenden Schritte deutlich zielgerichteter, als bei
einem reinen Telefongespräch besprochen werden. Daher bieten die
kARbon-Werkzeuge ein Mittel zur Reduzierung von
Missverständnissen, die sonst zu sehr kostenintensiven Fehlern
führen können.
Dies verringert zum einen den Kostenaufwand derartiger Treffen,
zum anderen können die Situation vor Ort und die
durchzuführenden Schritte deutlich zielgerichteter, als bei
einem reinen Telefongespräch besprochen werden. Daher bieten die
kARbon-Werkzeuge ein Mittel zur Reduzierung von
Missverständnissen, die sonst zu sehr kostenintensiven Fehlern
führen können.
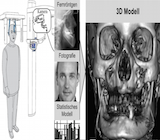
Kephalos
Orthodontic motivated radiographs substantial contributes to radiation exposure of children and adolescents. Especially since the introduction of dental digital volume tomography (DVT), the use of 3D radiographs is increasingly propagated. Because DVT devices typically generate 3D information from several hundred 2D radiographs, the effective dose of a DVT recording is at least an order of magnitude greater than that of a single digital lateral cephalogram. However, for many diagnostics a complete 3D model often is not needed, but only the outer (facial) surface of the facial skeleton. The aim of Kephalos is
to develope a new technique for calculating the exact facial
surface of the facial bones based on a) a single lateral
cephalogram, b) an optical face scan and c) a statistical model
of the correlation between the facial surface and the facial
bones.
The aim of Kephalos is
to develope a new technique for calculating the exact facial
surface of the facial bones based on a) a single lateral
cephalogram, b) an optical face scan and c) a statistical model
of the correlation between the facial surface and the facial
bones.Kephalos is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research.

KOLIBRI
The viability of small and cheap autonomous aircrafts opens up a whole new field of civilian applications. In this research project we are developing a low budget system to do research in the field the swarm behavior of small autonomous aircrafts. Our system is based on an affordable high speed optical tracking system with high accuracy and a software component for remote controlling arial vehicles, both systems are developed in our lab. Based on very small multicopters with a maximum weight of 50g, we investigate autonomous aircraft swarms and develop new algorithms to enable collaborative strategies for solving problems such as generating maps of an environment or identifying best paths to victims. The latest results can be found here.
LowDoseDVT
The aim of this research project is to develop algorithms that allow to calculate high quality three-dimensional reconstruction from cone beam computed tomography data needing fewer projection images than before. In this way the radiation dose for patients can be reduced significantly. In this project we follow three strategies in order to reduce the number of projection images needed. First, we carefully calibrate the geometric parameters of a cone
beam computed tomography machine. Second, we reduce
reconstruction artifacts by suitable processing the input
images. And third, we develop new regulized algebraic
reconstruction algorithms. For further information please visit
our project website.
First, we carefully calibrate the geometric parameters of a cone
beam computed tomography machine. Second, we reduce
reconstruction artifacts by suitable processing the input
images. And third, we develop new regulized algebraic
reconstruction algorithms. For further information please visit
our project website.

MILAN
Innerhalb des Forschungsprojekts MILAN wird die Infrastruktur ICARUS (Infrastructure for Compact Aerial Robots Under Supervision) des CVMR-Labors so zu erweitern, dass die darin verwendeten Multirotoren das Ausführen aggressiver Manöver erlernen. Diese dienen zum Beispiel dem schnellen kontrollierten Ausweichen in Gefahrensituationen, dem Durchführen von Mehrfach-Salti oder dem Minimieren der Flugzeiten beim Verfolgen vorgegebener Trajektorien. Der Fokus liegt dabei auf maschinellen Lernverfahren zur Verbesserung der notwendigen Bewegungsabläufe basierend auf Sensordaten und einem dynamischen Bewegungsmodell. ICARUS entstand im Rahmen der zuletzt geförderten Projekte KOLIBRI und ESCAPE, die in beiden vorangegangenen Jahren auf der CeBIT vorgestellt wurden und jeweils großes Interesse in den Medien fanden.
MTM Auto Code Generator
Methods-Time Measurement (MTM) is often applied in industrial settings whenever any manual operation or task is performed during the manufacturing process. It is used to analyze and optimize motion sequences of workers and thereby determine standard times in which a worker can complete the individual tasks. Thus one of the basic requirements of MTM is the ability to capture, and classify the movement of workers while executing these tasks. This research project aims to automate this by applying and fusing motion tracking methods based on various sensors. We develop a system to accurately capture the motion of
a worker, employed tools and components and simultaneously
segment and classify these motion sequences. For tracking
components and tools we investigate a novel optical passive
tracking algorithm since it is impractical to augment these
parts with any sensor or marker attachment in this setting.
We develop a system to accurately capture the motion of
a worker, employed tools and components and simultaneously
segment and classify these motion sequences. For tracking
components and tools we investigate a novel optical passive
tracking algorithm since it is impractical to augment these
parts with any sensor or marker attachment in this setting.

Multimedia Forensics
The massive growth of multimedia data poses challenges to law enforcement, who are confronted with analysing vast amounts of evidence in digital image and video form. Scenarios are the investigation of public desasters, or of cases of child sexual abuse. Here, multimedia analysis can support forensics by content classification, similarity search, or content clustering.iCOP project | sample paper (similarity search)
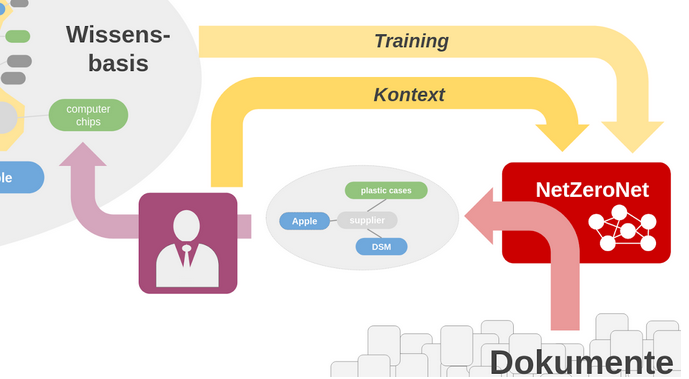
NetZeroNet
Angesichts des Klimawandels haben bewältigt die Industrie einen massiven Umbau ihrer Produktionsprozesse und Lieferketten. Im Zentrum steht das Ziel "Net Zero", das möglichst baldige Erreichen einer mindestens neutralen Nettobilanz an emittierten Treibhausgasen. Die Ausgangsfrage für das Projekt NetZeroNet ist das ungelöste Problem des umfassenden Screenings: Wie können Analysten technologisch bei der Bewertung von Unternehmen auf dem Weg zur Klimaneutralität unterstützt werden? Ziel ist die Entwicklung eines KI-basierten Prototyps, der es Analysten erlaubt die zunehmenden Informationsmengen, u.a. aus Firmenberichten, zu erschließen. Hierzu zeigt die KI Textstellen für den aktuellen Screening-Vorgang auf und extrahiert relevante Informationen. So erfassen Analyst und KI gemeinsam eine Wissensbasis die für zukünftige Sichtungen herangezogen werden kann, und die erstmalig auch indirekte Emissionen aus Wertschöpfungsketten ganzheitlich und branchenspezifisch erfasst. Hierbei verknüpft die NetZeroNet-KI das gewonnene Wissen direkt mit den zugrundeliegenden Textstellen, so dass diese nicht mehr aufwändig recherchiert werden müssen. Im Zusammenspiel mit den lernenden Assistenten von NetZeroNet können Domänenexperten somit die datengetriebene Analyse von Konsistenz und Vollständigkeit angestrebter und berichteter Treibhausgasemissionen effizient durchführen. So unterstützt das Projekt die Bekämpfung von Greenwashing und die Umleitung von Finanzströmen in nachhaltige Investitionen. NetZeroNet soll so die technologische Basis für ein neuartiges Datenprodukt für nachhaltiges Investment schaffen, das KI-gestützt skaliert und einen dedizierten Fokus auf Klimaneutralität bietet.
Dieses Projekt wird in Zusammenarbeit mit Sociovestix Ltd. durchgeführt. Es wird durch das Programm KI4KMU (FKZ: 01IS22050B) des Bundesministeriums für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) gefördert.
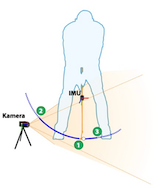
OPTIGAMA
The research project OPTIGAMA (Optical Short Game Motion Analyzer) is embedded in the research project SHOGAMA (Short Game Motion Analyzer) which is a joint project together with the Science & Motion Sports GmbH in Flörsheim and the institute of computer science of the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz. The aim of SHOGAMA is to develop a highly accurate realtime system for three-dimensional tracking of the golf cub during short game. The complete system will be composed of an inertial measurement unit (IMU) attached to the golfs cub handle as well as a camera observing the head of the golf cub. The aim of OPTIGAMA is to determine the golf cub position and orientation (pose) while it is inside the cameras field of view based on the camera footage. The determined pose can be additionally refined
and verified based on the data obtained by the IMU. On the other
hand pose information can be achieved only based on IMU data if
the golf cub is outside the cameras field of view. This
combination allows to monitor the complete golf stroke
mechanics.
The determined pose can be additionally refined
and verified based on the data obtained by the IMU. On the other
hand pose information can be achieved only based on IMU data if
the golf cub is outside the cameras field of view. This
combination allows to monitor the complete golf stroke
mechanics.
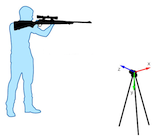
Optishot
Professionals who carry firearms on man (e.g. police officers), must be specially trained to deal with them. The training largely consists of repetition exercises in which the movement, including firing be rehearsed "process-safe". Existing measurement methods are very limited for a detailed analysis of the training shots and practical instructions to improve the sequence of movements. In addition, there is a disease (that is also known by golfer
and called "yips"), which may lead to occupational disability,
if it is not diagnosed early. In this research project we
develop a new measuring method which precisely determine and
evaluate the 3D movement and automatically creates instructions
to improve the motion sequence.
In addition, there is a disease (that is also known by golfer
and called "yips"), which may lead to occupational disability,
if it is not diagnosed early. In this research project we
develop a new measuring method which precisely determine and
evaluate the 3D movement and automatically creates instructions
to improve the motion sequence.
SCENT
SCENT (SCalable dEep Networks for business Text) addressiert den Einsatz neuester Deep Learning Techniken - sogenannter Transformer-Netze - zur Text-Analyse im Geschäftsumfeld von Banken und Versicherungen. Hier bietet sich angesichts einer enormen Skale an zu verarbeitenden Dokumenten (Nutzeranfragen, Versicherungsbedingungen und -Scheine) enormes Potenzial für ein KI-basiertes Textverstehen in wissensintensiven Geschäftsprozessen. In Zusammenarbeit mit den Firmenpartnern R+V Versicherung und Volksbank Mittelhessen sollen deshalb Techniken zur skalierbaren semantischen Ähnlichkeitsanalyse von Texten (z.B. Schadenbeschreibungen vs. Versicherungsbedingungen) sowie zur Informationsextraktion aus Kundenanfragen entstehen. Hier stoßen einerseits Heuristiken und einfache Lernverfahren an ihre Grenzen und sind der Vielfalt natürlicher Sprache nicht gewachsen. Andererseits sind Deep Learning-Methoden - während in der der Forschung seit neuestem etabliert - noch nicht direkt auf betriebliche Anwendungen übertragbar. Hier setzt SCENT an und erforscht Schlüsselaspekte wie mangelnden Annotationen (Few-Shot Learning), Skalierbarkeit auf Hunderttausende von Referenzfällen, sowie die Erkennung über lange Kontexten (z.B. Verteilung von Sachverhalten über viele Vertragsklauseln).
SCENT wird in Zusammenarbeit mit den Anwendungspartnern R+V und der Volksbank Mittelhessen, sowie den assoziierten Partner Cognaize und der SER Group durchgeführt. Als wissenschaftliche Partner begleiten das Deutsche Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz (DFKI) und die Universität Trier das Vorhaben. Dieses Projekt wird durch das Programm FH-Kooperativ des Bundesministeriums für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF) gefördert.

SHOGAMA
Im Rahmen des FuE-Projekts wird ein neuartiges System entstehen, mit dem die Bewegung eines Golfschlägers beim sogenannten Kurzspiel (Putten und Chippen) räumlich und hochpräzise erfasst werden kann. Dabei wird ein optisches, monokulares, passives Trackingverfahren in Kombination mit einer intertialen Messeinheit (englisch intertial measurement unit, IMU) entwickelt werden. Die beiden Sensorquellen gleichen hierbei jeweils ihre gegenseitigen Schwächen aus, um so den Messraum und die Messgenauigkeit des Gesamtsystems zu vergrößern bzw. zu erhöhen. Die Kamera wird so positioniert, dass sie die Schlägerbewegungen nahe des Balls, inklusive des Abschlags, mit maximaler Präzision erfassen kann. Sobald der Schläger den Sichtbereich der Kamera verlässt, wird die Bewegung mit der IMU anhand eines physikalischen Schlagmodells rekonstruiert. Der zeitliche Drift der den IMU Messdaten innewohnt, wird durch die absoluten Messungen der Kamera korregiert, sobald der Schläger wieder in deren Sichtbereich eintritt. Die Algorithmen werden auf einem eingebetteten System implementiert werden, welches dem Golfer innerhalb weniger Sekunden Feedback in Form einer 3D Visualisierung des Schlages liefert.
Die Hochschule RheinMain bearbeitet hierbei im Teilprojekt OPTIGAMA (Optical Short Game Motion Analyzer) im wesentlichen Fragestellungen im Bereich des optischen Trackings von Golfschlägern.
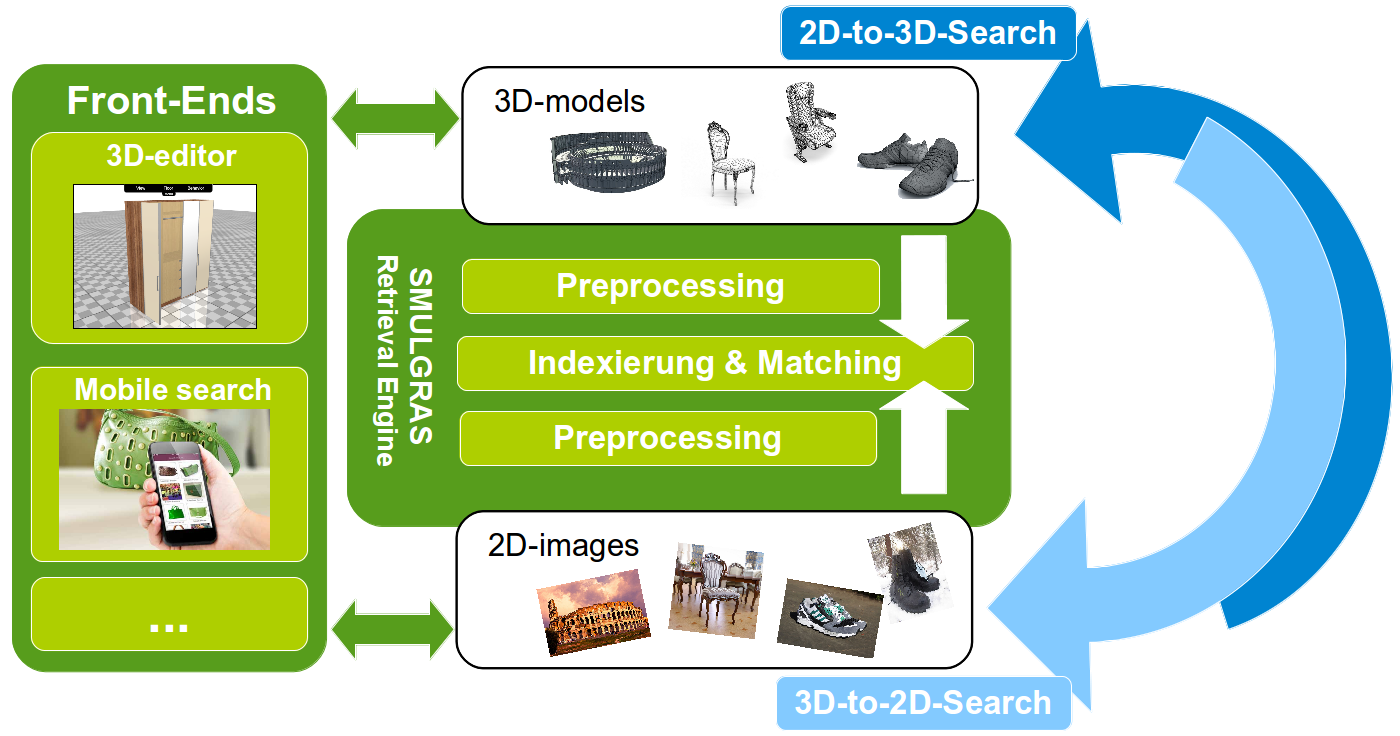
SMULGRAS
Content-based image search and 3D modelling are trending fields, with applications from copyright protection over mobile object search and 3D printing to community-based modeling. Key to exploiting large collections of images and 3D models, however, are efficient search and organization mechanisms. Here, SMULGRAS' goal is to investigate a multi-codal search between 2D images and 3D models: Given a camera snapshot, can we find the matching 3D model in a database? And given a 3D model, can we find images showing the corresponding object?
SMULGRAS is funded by the program Forschung für die Praxis and is executed in collaboration with Prof. Yvonne Jung from Hochschule Fulda and IntelligentGraphics GmbH.
web demo (request access per e-mail)

TECAN Bench
TECAN und HSRM erschließen in einer wissenschaftlichen Zusammenarbeit Synergien im Bereich optischer Überwachungsverfahren in der Laborautomation. Die Kooperation ermöglicht insbesondere dem wissenschaftlichen Nachwuchs der HSRM, an aktuellen und praxisrelevanten Fragestellungen zu arbeiten. Gegenstand des Projekts ist eines gemeinsames interdisziplinärer Projekt im Bereich der optischen Worktable-Erkennung.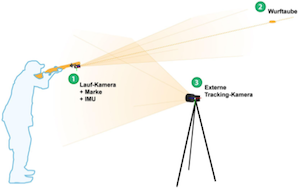
TRACKSHOT
The research project TRACKSHOT (Tracking of Shotgun and Target for Olympic Trap and Skeet) is a joint research project with the German Shooting Federation (DSB).The aim of the project is to detect and track the position and orientation (pose) of the shotgun together with the position of the target simultaneously in a common coordinate system. The resulting performance-diagnostic hardware component and a suitable software application should enable both the athlete and the trainer to have an accurate and timely evaluation and interpretation of the data. Beside the development of a robust and accurate marker-based tracking system, one of the main focuses of the project is to set the basis for a completely marker-less system, that enables tracking without the need of hardware to be attached to the sports equipment in order to have a completely non-reactive system. Particularly suitable for this initial tests for the development
of such a marker less optical tracking system is the shotgun due
to its size and thus good visibility. Thus, a feasibility study
for marker-less tracking is conducted within the project. If
this proves to be feasible, it would be dealt with in follow-up
applications for other sports equipment such as air gun or bow.
Particularly suitable for this initial tests for the development
of such a marker less optical tracking system is the shotgun due
to its size and thus good visibility. Thus, a feasibility study
for marker-less tracking is conducted within the project. If
this proves to be feasible, it would be dealt with in follow-up
applications for other sports equipment such as air gun or bow.

VEDUS
Many tasks in the field of urban planning, such as noise protection measures, the incidence of light, or radio coverage require 3D data. Complete 3D city models thus gradually replace conventional maps. But the creation and maintenance of 3D city models is very complex and costly. The goal of this research project is to develop a system that allow editing of 3D city models by various users using al kind of different devices. Users should be placed in a position to visualize and collaboratively edit the models on all kind of devices from the traditional desktop PC to Tablet PCs and smartphones.
Dieses Projekt (HA-Projekt-Nr. 315/12-05) wurde im Rahmen von Hessen ModellProjekte aus Mitteln der LOEWE – Landes-Offensive zur Entwicklung Wissenschaftlich-ökonomischer Exzellenz, Förderlinie 3: KMU-Verbundprojektvorhaben gefördert.
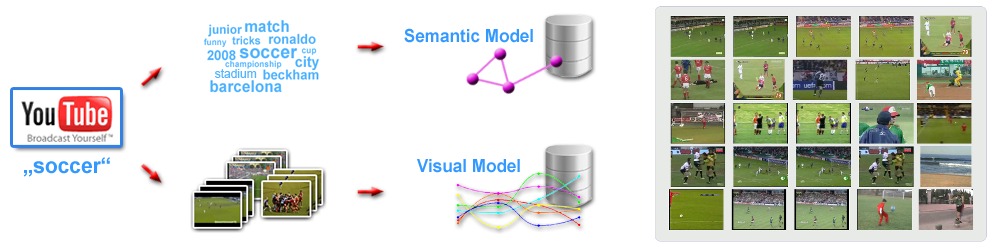
Visual Learning from the Web
Web-based portals like Flickr or YouTube offer huge amounts of images and videos, combined with rich context (such as tags, descriptions, comments, ratings, etc). This information can be exploited for a multi-modal auto-understanding of web-based multimedia. By training visual recognition systems at larger scale and combining their output with other signals, smarter search and recommendation can be facilitated. Core research issues are learning from unreliable labels, domain drift, and new forms of supervision to learning.MOONVID project | demo | sample paper (demographics prediction)

WASABI
WASABI brings together computer vision experts from HSRM with colleagues from the National University University of Sciences and Technology (NUST) in Islamabad / Pakistan. Pakistan ranks third in water scarcity world-wide, and suffers from a lack of proper water resource management. While drying up on the one hand, the country experiences catastrophic floods on the other. Therefore, to better manage water resources so that to enforce an even distribution of water throughout the year, a solution is required to densely supervise the volume of water bodies (including rivers, lakes, and reservoirs) and predict the ratio at which the water resources are varying. To this end, the project WASABI (WAter resource estimation by SAtellite Based Image analysis) aims at laying the foundations for a system that quantitatively monitors Pakistan’s water bodies and helps national authorities with a more proactive water supply management. To do so, the WASABI system will employ remote sensing satellite imagery of Pakistan’s water bodies. This data will be processed with state-of-the-art machine learning / deep learning techniques to estimate the current quantity of water and - based on historic time series of population and seasonal capacity fluctuation - predict the amount of water available in the near future. WASABI‘s core research challenge lies in the fact that labeled data for Pakistani waterbodies is scarce, which is why unsupervised learning and transfer learning from
densely labeled regions such as Europe will be explored. The
project also features an academic exchange program, with interns
from NUST visiting Wiesbaden on an annual basis.
which is why unsupervised learning and transfer learning from
densely labeled regions such as Europe will be explored. The
project also features an academic exchange program, with interns
from NUST visiting Wiesbaden on an annual basis.